The application of web-based multiplayer educational games in education is directly connected with the theory of constructivism, according to which learning brings change in a meaning that is created based on already gained knowledge. The relevant theory that must be taken into consideration during games design states as follows:
· All knowledge is constructed instead of delivered.
· Knowledge and the corresponding meanings derive from activities.
· Knowledge is shared amongst people, tools and other objects.
· Meanings arise from the interpretation of knowledge and related activities, and thus, multiple perspectives are identified.
· The construction of meanings is dictated by the problems, questions and authentic tasks.
Taking the above into consideration, the game will follow the methodology shown in Figure 1.
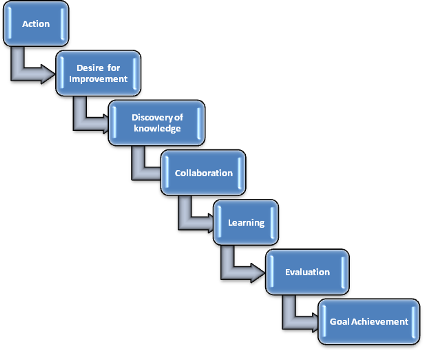
Figure 1. Methodology steps
More specifically, the game always starts with a specific action. This action is attractive enough that it highlights students’ desire to improve by participating on the action’s given steps. Through this motivation process, students discover knowledge within the game. This is realized through a series of tasks that provide segments of computer programming information. These tasks are completed through collaborative work. This way, the game will not only support students gaining knowledge, but also them developing various skills (e.g. group work, task allocation, organization etc) that will benefit them in their future professional lives. The constant collaborative undertaking of these tasks will lead to learning of the taught elements. This learning will then be evaluated with a number of assessment measures established by teachers. If the evaluation results are above the set average, then it is considered that the targeted learning outcomes are achieved.